This document describes
For information about problems and workarounds, see the Known Problems and Solutions.
Before installing, first close all applications that use OpenAccess libraries.
Then make sure that there are no oaLibServer or oaFSLockD
processes running (kill these processes with the kill command).
The tarkits containing source code, public includes, and documentation are platform independent.
| Full Tarkit Name | OpenAccess Components |
|---|---|
oaSrc_<rel>_all.tar.gz |
OpenAccess source code |
oaInc_<rel>_all.tar.gz |
OpenAccess public includes |
oaDoc_<rel>_all.tar.gz |
Documentation and programming examples |
The tarkits containing the libraries and binaries are platform specific.
| Full Tarkit Name | OpenAccess Components |
|---|---|
oaDev_<rel>_<platform>.tar.gz |
Debuggable libraries, debuggable binaries, plus both debuggable and optimized archives |
oaRun_<rel>_<platform>.tar.gz |
Optimized libraries and binaries |
If you want a runtime version of OpenAccess, simply download the oaRun tarkit for your platform.
If you want a developers version including the documentation and examples, download the oaDev tarkit for your platform, plus the following platform-independent tarkits:
Important: Do not move directories or files within the OpenAccess installation hierarchy. This will result in problems with your installation. Also, do not mix kits from different releases.
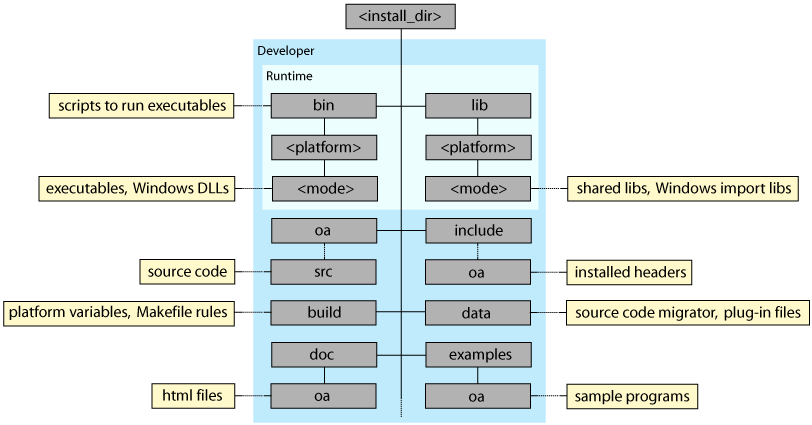
The following figures shows the main components of the OpenAccess 2.2 installation hierarchy.

For information about the naming conventions for <platform>
and <mode>, refer to OpenAccess
Installation Hierarchy in What's New in OpenAccess.
The SPEF and LEF/DEF translators require zlib to run (Windows platform only).
lib directory to your PATH
environment variable.
zlib into C:\zlib1.2.1,
use:
C:\zlib1.2.1\lib;OpenAccess provides specific levels of compatibility between releases. Two types of compatibility are provided:
For more information, refer to Compatibility for OpenAccess Applications and Data.
All applications in a flow must be capable of supporting the highest data model used in that flow. There are several ways you can specify the supported data model when importing data using OpenAccess translators.
OA.DATAMODEL in the data
directory of your OpenAccess installation hierarchy.
OA_DATAMODEL environment variable to specify the highest
data model supported by your flow. For example, set the environment variable as
follows to indicate that your flow does not yet support the incremental
technology database feature:OA_DATAMODEL 2
-dataModel option of the strm2oa, lef2oa,
or def2oa translator to specify the data model when importing data
into OpenAccess.
The OA_DATAMODEL environment variable overrides a value set in the
OA.DATAMODEL file. In addition, the individual -dataModel
translator options override the value set by either the environment variable or
an OA.DATAMODEL file. If you use the OA.DATAMODEL file
or the OA_DATAMODEL environment variable to specify the highest
data model supported by your flow, the translators default to this value when
importing data into OpenAccess.
When reading data into OpenAccess, the translators adjust their output based on the specified data model. For example, if data model 1 is specified (by any of the three mechanisms above), and the design data to be imported contains new constraints from data model 2, those constraints will either be saved as properties instead of as OpenAccess constraints or dropped. For more information about how data is handled in such situations, refer to the mapping documentation for the translators.
If you want to link against the OpenAccess pre-compiled libraries, you must use the compilers in the following table.
| Redist kit | Platform | Compiler |
|---|---|---|
| sol86 | Solaris (x86_64) Operating System 10
with support for STLPort4 C++ standard template libraries |
Solaris Compiler: Sun Studio 11 C++ 5.8 |
| sun4v | Solaris Operating System 10
with support for STLPort4 C++ standard template libraries |
Solaris Compiler: Sun Studio 12 C++ 5.9* |
| lnx86 | Linux (x86 and x86_64) Operating System: Red Hat
Enterprise Linux 4.0
Compatible with: RHEL50, SLES 10, SLES11 |
Linux Compiler: gcc 4.4.3 |
| wint | Windows Operating System: Windows 2000/XP | Windows Compiler: Visual Studio 2005 |
| ibmrs | IBM Operating System: AIX 5.3 | IBM Compiler: XL C++ 7.0 |
| Notes |
* For sun4v systems for Solaris
10, the following variable must be set: setenv OA_COMPILER stl4
|
| 32 bit OA libraries are now compiled without the PIC option on Solaris and Linux. |
The required GNU make utility is:
GNU
makeversion 3.80
Earlier versions of the GNU make utility do not work correctly with
the GNU makefiles supplied with OpenAccess. Refer to
http://www.gnu.org/software/make for information about downloading the
GNU make utility.
Important: It is recommended that you rename the make utility
as gmake. This will prevent older, incompatible versions of make
from being called.
Set your
pathvariable to point to the location of your OpenAccess binaries so that you can execute the binaries from any directory:
<install_dir>/bin/win32/opt
The OpenAccess UNIX binaries have wrapper scripts to automatically set appropriate environment variables. On Linux, you must set the LD_LIBRARY_PATH variable to include the directory containing the correct version of
libstdc++.so, which is described in Optionally Compiling on UNIX Platforms (Solaris, IBM, and Linux).
You can set your path environment variable to point to the location of the OpenAccess wrappers in the top-level bin directory of your installation:
<install_dir>/bin/The generally accepted installation location for
<install_dir>is/opt/OpenAccess. You need to install as root on UNIX in order to use the default installation path.Unsupported Platforms
For UNIX platforms, you can build on an unsupported platform by setting the environment variable
OA_UNSUPPORTED_PLATfor your platform. Note that this environment variable will not override a recognized supported platform.To determine how to set
OA_UNSUPPORTED_PLAT, do the following:
- In the bin directory, type
./sysname.
This script returns the string that must be overwritten with theOA_UNSUPPORTED_PLATvariable.
- Set the environment variable to the correct string.
For example, if the binary directory that exists islinux_suse9_32, but the wrapper scripts are looking forlinux_rhel30_gcc411, you should setOA_UNSUPPORTED_PLATtolinux_suse9. (The_32portion is automatically set and should not be part of the name you use.)Overriding Environment Variables
The debug versions of the shared libraries perform additional checking that is not available in optimized libraries. For more information, see OpenAccess Overview.
To run all the binaries in debug mode:
setenv OA_MODE dbgTo set the mode to debug for a single binary, use the name of the executable in all capital letters, followed by
_MODE. For example:setenv DEF2OA_MODE dbgTo set the mode to 64-bit for all binaries (SUN, or IBM platforms only):
setenv OA_BIT 64Note: On Opteron, the default is 32, but will revert to 64 if the 32-bit version is not available.
To set the mode to 64-bit for a specific binary, use the name of the executable in all capital letters, followed by
_BIT(SUN, or IBM platforms only). For example:setenv DEF2OA_BIT 64
Pre-compiled versions of all the OpenAccess libraries are included in your installation. You might want to recompile these libraries in order to port to a new platform or verify a bug fix. You might also want to use a different compiler of your choosing. When you recompile the OpenAccess libraries, the translators, extensions, and the package containing the functions common to the translators are also recompiled.
Important:
make version 3.80 is required. (It is recommended that you
rename the make utility as gmake. This will prevent older,
incompatible versions of make
from being called.)
The following table shows the default compiler environments for OpenAccess. The compiler environment is controlled with a platform-specific configuration file included in your installation.
If your compiler is in a location other than the default, create a symbolic link from the default path in the table to the location of your compiler.
| Platform | Compiler | Configuration File | |
|---|---|---|---|
Solaris 10 STLPort4
|
Sun Studio 11 C++ 5.8 |
|
|
| Default Path | /opt/SUNWspro/v11/SUNWspro/bin/CC |
||
| Compiler Version | Sun C++ 5.8 Patch 121018-16 2008/06/25 | ||
Solaris 10 STLPort4,
|
Sun Studio 12 C++ 5.9 |
|
|
| Default Path | /opt/SUNWspro/v12/SUNWspro/bin/CC |
||
| Compiler Version | Sun C++ 5.9 SunOS_sparc Patch 124863-11 2009/03/10 | ||
|
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4.0, 32-bit or 64-bit |
Linux Compiler: gcc 4.4.3 |
|
|
| Default Path | /opt/gcc4.4.3/bin/g++
|
||
| Compiler Version | gcc (GCC) 4.4.3 | ||
|
IBM AIX 5.3,
32-bit or 64-bit |
IBM Compiler: XL C++ 7.0 |
|
|
| Default Path | /usr/bin/xlC_r |
||
| Compiler Version | vacpp.cmp.core 07.00.0000.0007 C F IBM XL C/C++ Compiler | ||
The compiler versions indicate the minimum version. To determine the compiler version for a system, use the following commands.
| Platform | Command | |
|---|---|---|
Solaris |
CC -V |
|
Linux |
gcc --version |
|
| IBM AIX 5.3 | xlC_r -qversion
|
|
You compile OpenAccess as follows. (If you want to compile on a Linux platform not listed above, refer to Optionally Compiling on an Unqualified Linux Platform before proceeding.)
setenv SYSNAME_OPTIONS _64
Note: On Opteron, this is automatically set to _64.
You can force it to _32.cd <install_dir>/oagmake <command> OPTMODE=<mode> VERBOSE=<state>
<command>can operate on the entire OpenAccess distribution including all subpackages and translators, or just the OpenAccess core packages.install_allEntire distribution* clean_alluninstall_allinstallCore packages cleanuninstall<mode>is one of:dbgDebug compile, which is the default optOptimize compile <state>is one of:falseHide compile commands, which is the default trueShow compile command
* There are prerequisites for building the translators and other non-core packages. Refer to Prerequisites for Compiling Translators and Other Non-Core Packages for more information.
Recompiling the OpenAccess libraries does not mean that you must also recompile the translators. However, note that the translators and the OpenAccess libraries must be built with the same compilers in order to work together.
* There are prerequisites for building the translators and other non-core packages. Refer to Prerequisites for Compiling Translators and Other Non-Core Packages for more information.
Refer to Prerequisites for Compiling Translators and Other Non-Core Packages if you get compilation errors related to the translators, oaTcl, or other non core packages.
After you compile OpenAccess, you can test your build by running the supplied unit tests.
cd <install_dir>/oa/test
gmake unitTest OPTMODE=<mode> VERBOSE=<state> >
& test.out &If you want to compile OpenAccess on a platform not listed in Supported Platforms and Compilers for OpenAccess Pre-Compiled Libraries, complete the following:
sysname shell script to return the <platform_name>
for your platform. Note that this script is overwritten when you install a new
version of OpenAccess.
sysname shell script is located at <install_dir>/build/bin.
OA_UNSUPPORTED_PLAT environment variable. See
Unsupported Platforms for more information. With this approach, the
information is not lost when you install a new version of OpenAccess.
<platform_name>_<bit>.variables
<platform_name> is the name you chose in
Step 1, and <bit> is either 32 or 64 (to represent
either a 32 or 64-bit operating system).
<install_dir>/build/make
to determine the content required for your file.Proceed to Optionally Compiling on UNIX Platforms (Solaris, IBM, and Linux).
Pre-compiled versions of all the OpenAccess libraries are included in your installation. You might want to recompile these libraries in order to port to a new platform or verify a bug fix.
Note: Recompiling the OpenAccess libraries does not mean that
you must also recompile the translators, such as verilog2oa.
However, note that the translators and the OpenAccess libraries must be built
with the same compilers in order to work together.
Use Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 to compile your environment on
Windows. The OpenAccess solution files for Visual Studio 2005 have a _vc8
extension in their name.
oaDynamic_vc8.sln is for Visual Studio 2005OpenAccess provides a solution file that you can use to rebuild OpenAccess. You might do this if you want to test changes to the OpenAccess API on your local machine.
The following solution lets you compile and build dynamically on all source packages, and includes an oaTest.exe that includes all the unit tests (oaBaseTest, oaDesignTest, oaReticleTest, oaTechTest).
<install_dir>/oa/oaDynamic_vc8.sln
To build:
oaDynamic_vc8.sln (for Visual Studio 2005)
You can also build on the command line. For example, the following command
creates an optimized version of OpenAccess and outputs the build information to
out.log:
devenv oaDynamic_vc8.sln /build optDLL /out out.log
Run oaTest.exe to test your environment. The testLog.txt
log file and the unit test libraries are at <install_dir>/oa/test/testDir.
The oaStrm, oaLefDef, and oaVerilog translators can be compiled similarly.
However, it is rarely necessary to compile the translators. The executables
have already been provided.
If you want to develop an application using OpenAccess, you can create your own Visual Studio solution to include the headers and libraries that you want. Provide Visual Studio with the following OpenAccess paths:
| Files | Path |
|---|---|
| Executable files | <install_dir>\bin\win32\<mode> |
| Include files |
<install_dir>\include\oa |
| Library files | <install_dir>\lib\win32\<mode> |
To set these paths in Visual Studio:
OpenAccess depends on the Winsock2 socket technology, and therefore must include Winsock2.h.
If your code files contain #include <Windows.h> statements,
you must do one of the following:
#include
<Windows.h> statement.
#include <WinSock2.h> statement before the #include
<Windows.h> statement.Note that most users do not specify #include <Windows.h> statements
in their code files because OpenAccess code files already contain include
statements for Windows.h.
Very few users need to recompile the OpenAccess translators. You need to do this if you use an operating system that is not compatible with one of the pre-built versions, or if you want to modify the distributed translator. Third-party packages are required in order to build the translators.
LEF and DEF
Unless you have the LEF/DEF parser kits and zlib installed, you will get errors on LEF/DEF translator compilation.
Download and compile the 5.70 or later LEF/DEF parser from http://openeda.si2.org/projects/lefdef/. The makefiles for the LEF/DEF translators supplied by OpenAccess expect the LEF/DEF parser to be installed in
/opt/lefdefInt/v<version>. To satisfy this requirement, do one of the following:
- Specify a
LEFDEF_HOMEenvironment variable to override the default location. You can also specify LEF and DEF paths individually withLEF_HOMEandDEF_HOME.- Copy the files to the correct locations:
- The LEF/DEF parser header files must be copied into
/opt/lefdefInt/v<version>/tools.<platform>/include.- The 32bit LEF/DEF parser libraries must be copied into
/opt/lefdefInt/v<version>/tools.<platform>/lib.- The 64bit LEF/DEF parser libraries must be copied into
/opt/lefdefInt/v<version>/tools.<platform>/lib/64bit.You must also install the
zlibpackage from: http://www.gzip.org/zlib/
The OpenAccess LEF and DEF translators were qualified usingzlibversion 1.2.3.On UNIX, the
ZLIB_HOMEvariable defaults to/opt/zlib/v1.2.3(for 32-bit execution) and/opt/zlib/v1.2.3_64(for 64-bit execution).On Windows, you must set the
ZLIB_HOMEenvironment variable to point to thezlibinstallation directory. In addition, set the OA_DEP_LIBS environment variable to point to the directory containing your LEF/DEF parser kits (lefdefInt). The default version of the LEF/DEF parser kits is specified in <install_dir>/build/MSVS/dep.vsprops. Modify this file if you need to override the default version.Note: The OA_DEP_LIBS environment variable overrides any LEFDEF_HOME environment variables.
See the OpenAccess release notes for information about limitations for LEF and DEF in this release.
OpenAccess to SPEF Translator
If you want to compile your own version of the SPEF translator, you must install the
zlibpackage from: http://www.gzip.org/zlib/
The OpenAccess SPEF translator was qualified usingzlibversion 1.2.3.On Windows, you must set the
ZLIB_HOMEenvironment variable to point to thezlibinstallation directory. On UNIX, theZLIB_HOMEvariable defaults to/opt/zlib/v1.2.3(for 32-bit execution) and/opt/zlib/v1.2.3_64(for 64-bit execution).OpenAccess to Verilog Translators
If you want to compile your own versions of the Verilog translators, you need the following tools:
- Bison 1.875 source and executables (http://sourceforge.net/project/showfiles.php?group_id=23617&package_id=22822)
- Flex++ 2.5.4 source (http://www.gnu.org)
Note: Flex++ is included with the Flex package.Use the environment variables BISON_HOME and FLEX_HOME to specify the installation root of the Bison and Flex executables. (It is expected that the executables will be in the
bindirectory under the installation root).
Environment Variable Windows Default UNIX Default BISON_HOME C:\Program Files\GnuWin32
/opt/bison/v1.875FLEX_HOME None /opt/flex/v2.5.4OpenAccess Tcl bindings
Unless you have Tcl installed, you will get errors for oaLang compilation, which contains the OpenAccess Tcl bindings. For information about compiling the OpenAccess Tcl bindings, refer to Tcl Bindings for OpenAccess APIs.
The Tcl OpenAccess API is available in Tcl version 8.4.6. and later. In order to use the Tcl OpenAccess API in Tcl, you must install Tcl 8.4.6. or later. You can obtain Tcl from:
Set the TCL_HOME environment variable to the location of your Tcl installation. The default TCL_HOME path is:
/opt/tcltk/v8.4.6.oa20to22 Translator
- If you do not already have a OpenAccess 2.0 installation, download and install the 2.0 kits.
- Download the following kit for the platform you want:
OACommon
- Expand this kit in the directory that contains your OpenAccess 2.0 hierarchy.
- Set the environment variable
OAHOME_2_0to the directory that contains the expanded kits and the OpenAccess 2.0 hierarchy.
- Add the directory that contains the cdsCommon executables (typically
tools.<platformName>/bin) to your executable search path.
UNIX Platforms (Solaris, IBM, and Linux)
Use the rm -r command to remove your installation hierarchy:
% rm -rf <install_dir>

Copyright © 2003-2006
All rights reserved.