 |
 |
 |
||||||
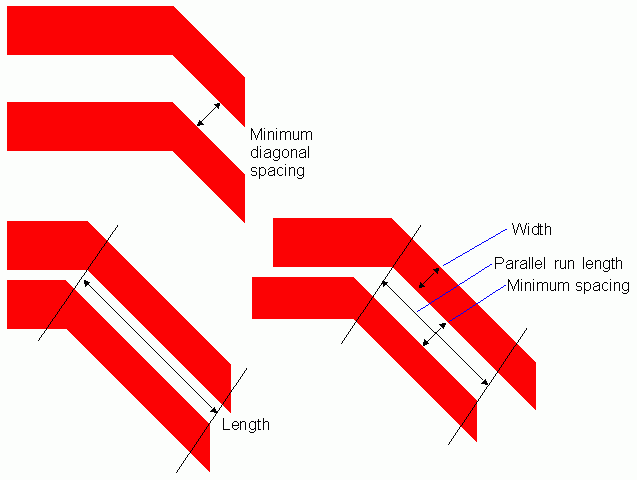
The built-in layer constraint definition oacMinDiagonalSpacing determines the minimum diagonal distance required between any two geometries on the specified layer. The distance is specified in database units and should be calculated as the actual or Euclidian diagonal distance, not the Manhattan distance.
| Constraint type: | oaLayerConstraint |
| Value types: | oaIntValue, oaInt1DTblValue, oaInt2DTblValue |
| Database types: | oaDesign, oaTech |
| Object types: | oaAppObject |
The following value types are supported by this constraint:
If the oaIntValue is specified, the value represents the minimum diagonal spacing required between the two geometries in database units.
Units: DBU
If an oaInt1DTblValue is specified, the lookup key ("width") in the table represents the width of the wider of the two shapes, and the value for the table represents the minimum diagonal spacing required between the two shapes in database units. The width of the shape is defined as the smaller of the shape's two dimensions.
Units: DBU
If an oaInt2DTblValue is specified, the row lookup key ("width") in the table represents the width of the wider of the two shapes, the column lookup key ("length") in the table represents the parallel run length between the two shapes, and the value for the table represents the minimum diagonal spacing required between the two shapes in database units. The parallel run length between the two shapes is calculated as the distance in the lengthwise direction for which the two shapes are directly orthogonal (meaning that a line running perpendicular to the length would intersect both shapes).
Units: DBU
Minimum spacing constraints help to ensure that geometries are not merged together during fabrication.
Copyright 2002 - 2010 Cadence Design Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.